Structural Audit in Mumbai- Things to know
If you have come across the term ‘Structural Audit’ in relation to a structure, read further to know it’s purpose, the process and the tests it comprises of. An Authorized/Licensed Structural Engineer of the city audits the structure from strength, serviceability and maintenance point of view.
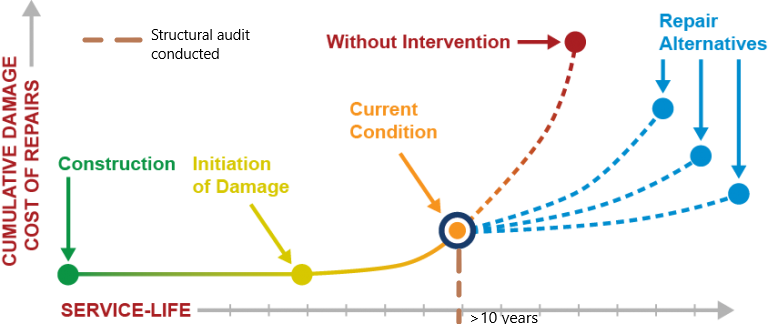
Every once in a while, a building requires regular health check-ups just like a human body. Just like a doctor would diagnose the problems using X-Rays, MRIs, Blood tests, etc., a structural auditor conducts various tests to diagnose the health of structure. Regular audit and maintenance not only help in keep the safety of the structure intact, but also helps keep the costs of maintenance down over the years. Generally, the design life of a structure is around 40 to 50 years, based on the intended use. Here is a look at the life cycle of a building and how conducting structural audit at regular intervals can help keep the maintenance costs down.
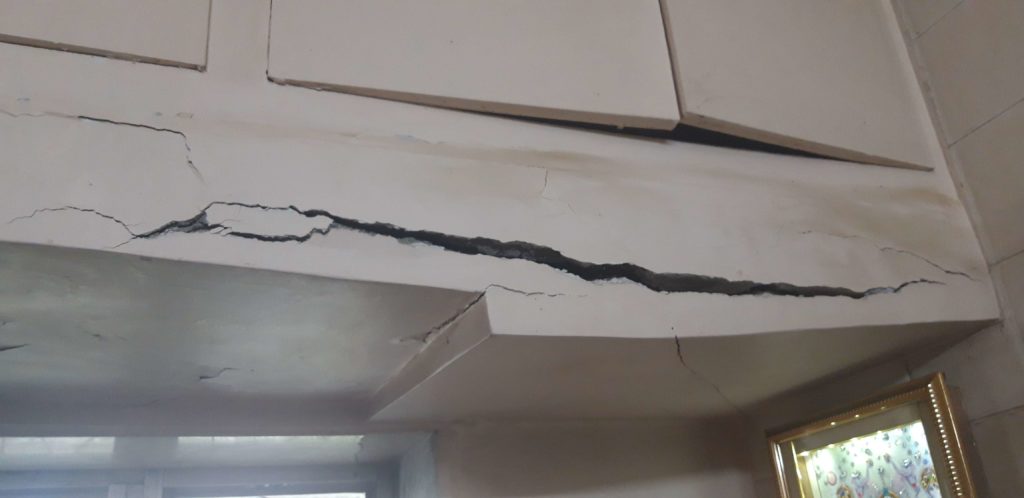
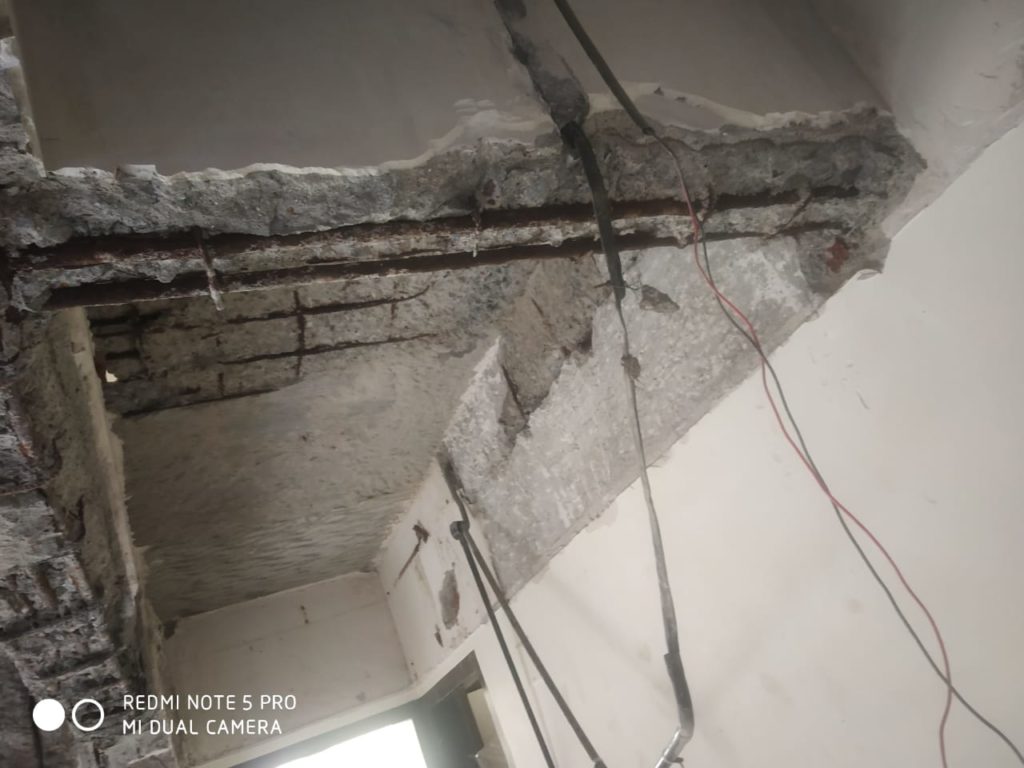
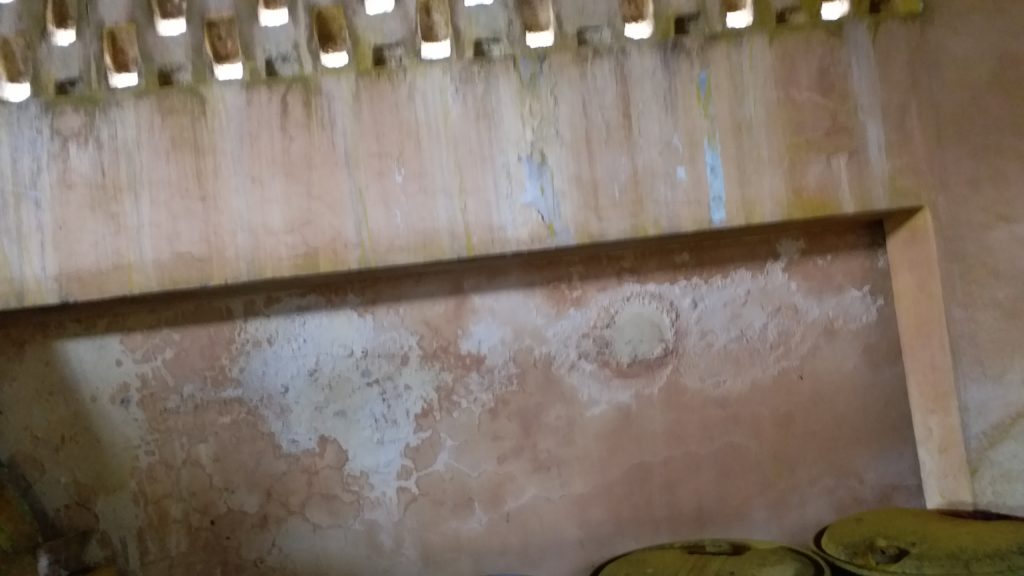
Signs of Distress
A typical RCC structure shows some signs of deterioration as it ages and they become alarming towards the second half of its service life. For e.g.-
- frequent leakages,
- dampness in ceilings and walls,
- cracks in RCC members,
- jamming of door and window frames,
- excessive deflection in slabs or beams,
- spalling of concrete, corrosion, etc.
On the other hand, a steel structure shows the following signs-
- Rusting of steel members and connections, especially in corrosive environments,
- Local buckling,
- Discontinuity in welding,
- Excessive deformations or vibrations, if put to use for loads beyond design consideration, etc.



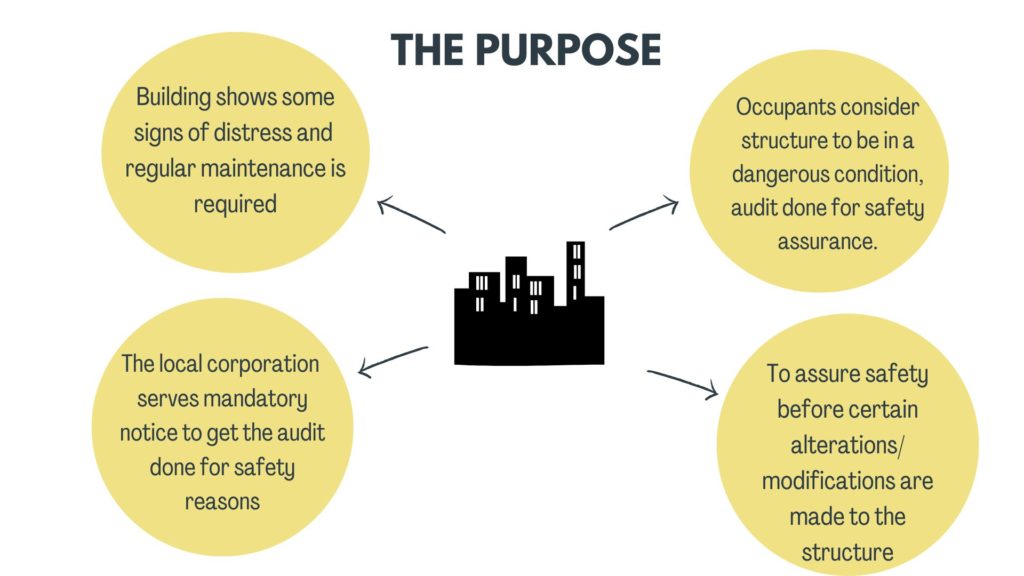
When to conduct a structural audit?
When and why to conduct a structural audit must be decided by the occupants/owners of the structure. It could be done for any of the following reasons. Audit is also a crucial factor in the cost-benefit analysis of repairing & renovating vs. demolishing and constructing a new one.
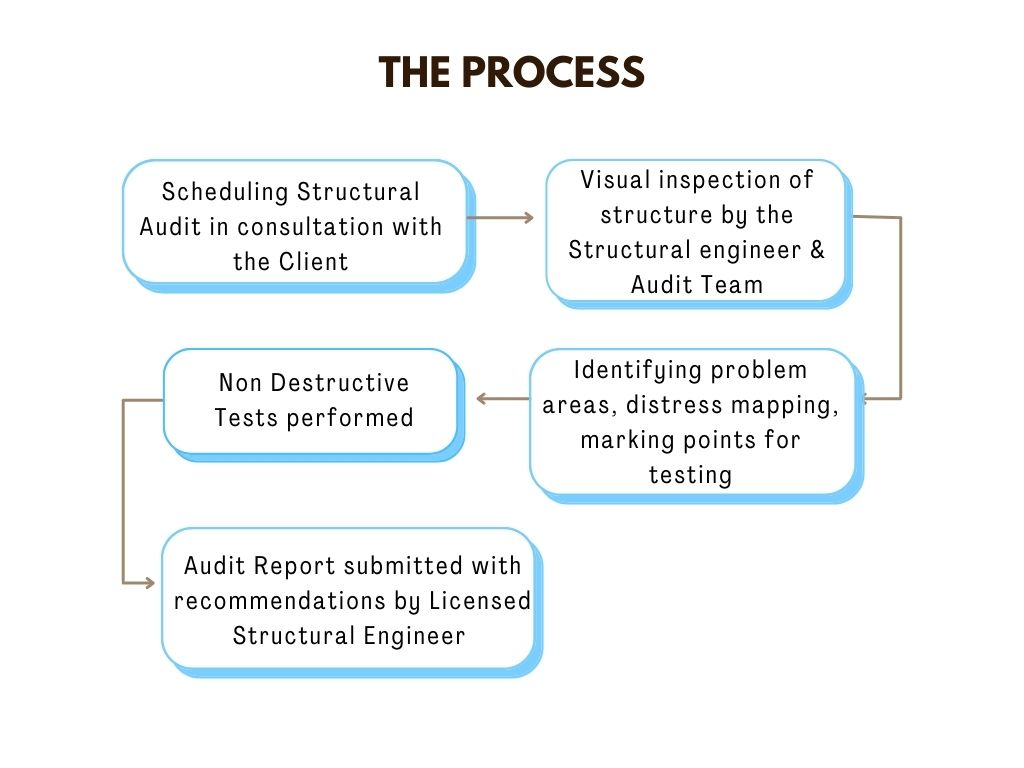
How is it conducted?
To conduct a structural audit, an MCGM licensed Structural Engineer is appointed. It is important to inform the auditor of all the distress signs, relevant history of the structure, findings of previous audit, if any, etc. A full structural audit involves survey of the structure, inspection of structural components and their testing. The tests being ‘non-destructive’ in nature are often called NDTs as the structural integrity of the building is not harmed.
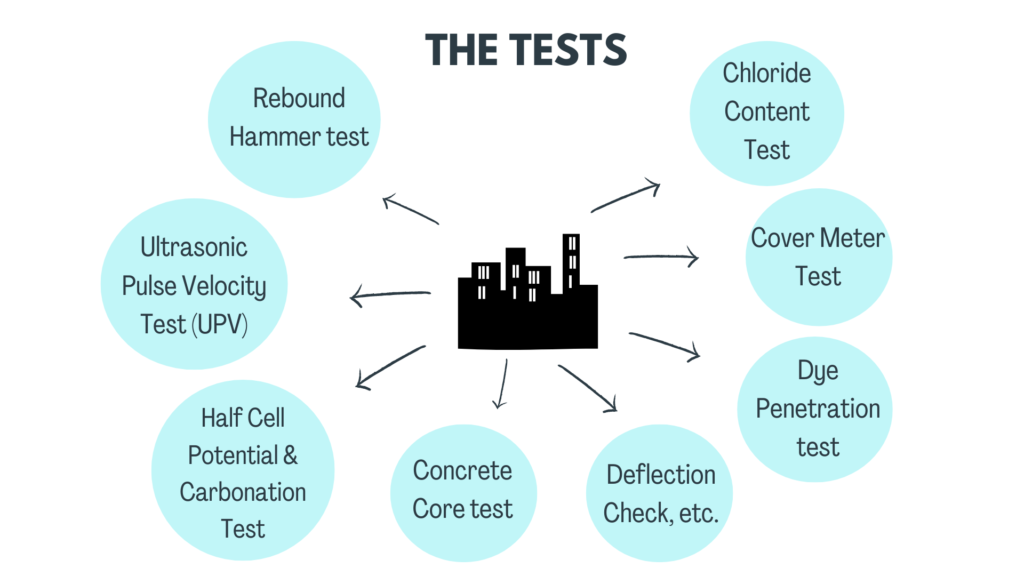
Risk assessment in a structural audit
The Structural Engineer inspects the structure for problem areas, risks due to alterations to structure, extent of corrosion, seepage and identifies structural cracks from non-structural ones. Non-Destructive Tests (NDTs) are performed for determining the integrity and strength of the concrete (Rebound Hammer Test, UPV Test, Concrete Core test), to determine extent of corrosion of reinforcement (Half-cell Potential and Carbonation test), to determine the positions of existing reinforcement and cover (Cover meter test), Crack width measurement, Radiography and Dye Penetration Test for steel structures, etc.
Finally, the Structural Engineer provides a detailed report stating observations, test findings, distress maps and conclusions. The report,presented in the required format of MCGM, also states recommendations for repairs or solutions, which must be followed to keep the building in good shape and extends its service life. Keep in mind, this report is has legal implications, especially in matters of disputes. In conclusion, structural audit must not be considered optional, but as a necessity to extend the service life of structure and avoid any impending failures.
Cost of Structural Audit
Structural audits are complex and must be performed by competent engineers. The cost of conducting a structural audit depends on the scope of work, structure geometry, number of storeys of building, area of premises, expertise of engineers and technicians and cost of tests involved. To know exact cost of audit of your structure, contact us and get an exact quote within 24 working hrs.